分形
分形(Fractal)是一个有趣的数学现象,即存在这样一种图形,它的局部与全体具有一定的相似性。也就是说,对于一个具有分形性质的图形,它可以无穷放大而具有相似的图形模式,
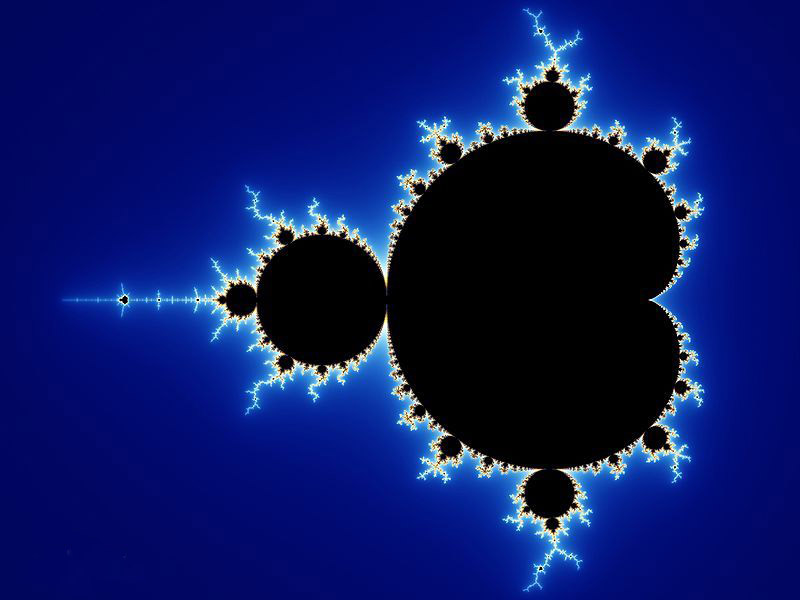
如果有这么一样东西,不管你怎么放大它,看到的都是相似图案的循环,在放大10000倍的一个角落里,居然出现了和整个物体相同的花纹,这是多么美妙的图案!
Mandelbrot 集就是一个经典的分形图案,它由一个简单的多项式迭代生成:
\[z_{i+1}=z_i^2+c\]这其中 $z,c$ 是复数,$z_0=0$,序列的值或者延伸到无限大,或者只停留在有限半径的圆盘内。Mandelbrot 集合就是使以上序列不延伸至无限大的所有 $c$ 的集合。
还有另一个经典的分形使用与上面一样的迭代公式和方法——Julia 集,不过在 Julia 集中,$c$ 是一个常复数,Julia 集合是使以上序列不延伸至无限大的所有 $z_0$ 的集合。
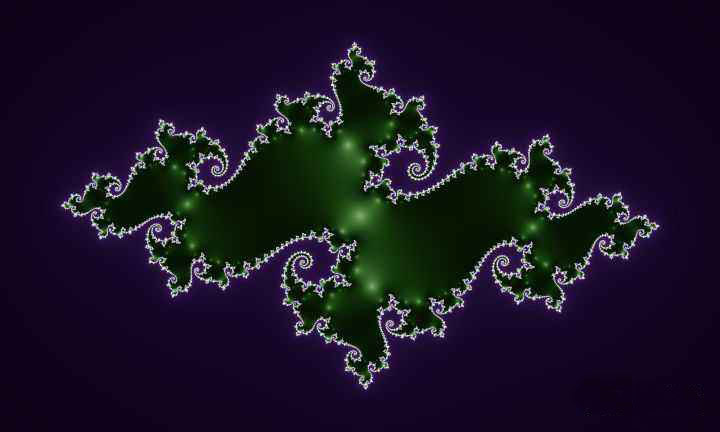

简单程序实现
由于这两种分形集合使用简单的公式和迭代方法,尤其适合程序实现。
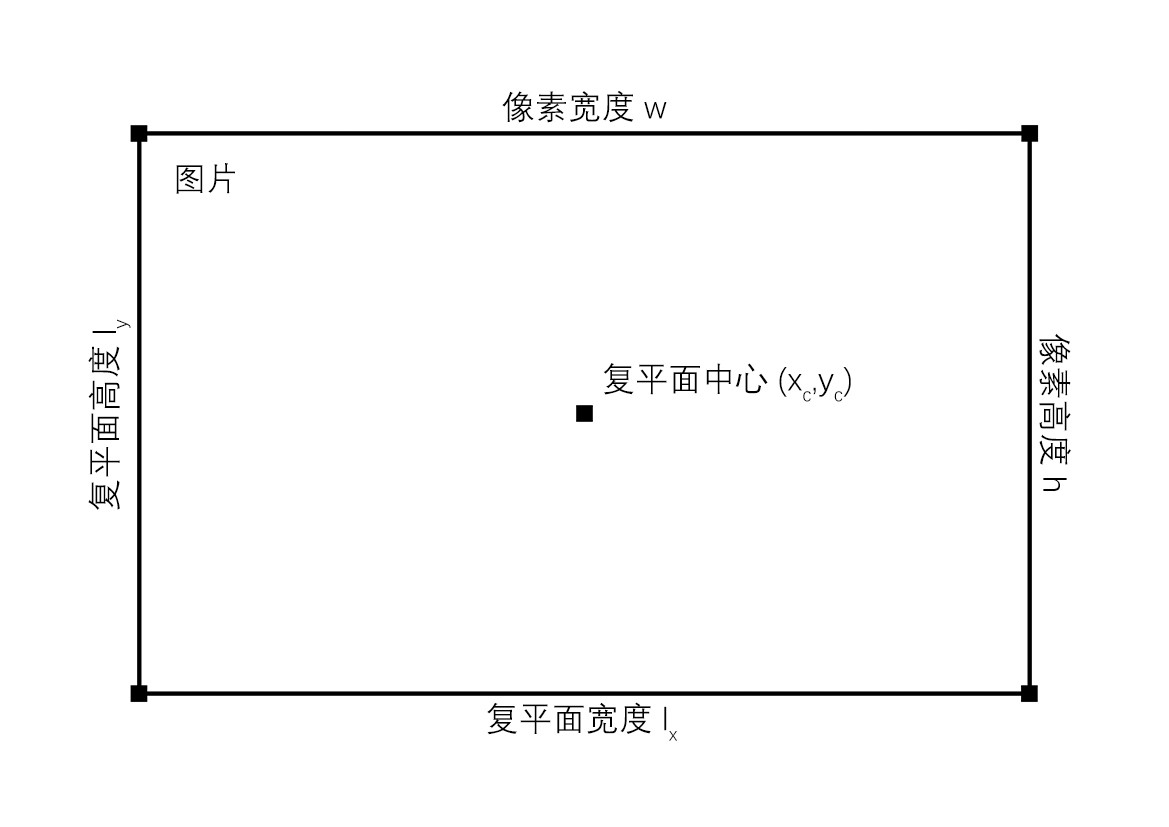
通过设定图像宽度对应的 $x$ 轴区间长度和图像中心点对应的复平面位置,我们可以获得图片像素到复平面上的值的映射。
设图片宽 $w$,高 $h$,中心位置 $(x_c,y_c)$,宽度对应的区间长度 $l$,如图示:
容易得到
\[\begin{gather} l_x=l\quad l_y=\frac {hl}w\\ x_l=x_c-\frac l2\quad x_h=x_c+\frac l2\\ y_l=y_c-\frac {hl}{2w}\quad y_h=y_c+\frac {hl}{2w}\\ x(i)=x_l+\frac{l_x}{w}i\\ y(j)=y_l+\frac{l_y}{h}j \end{gather}\]这样一来我们就完成了图片上的像素到复平面上的值的映射。
在程序中,我们无法判断一个序列是否要发散到无穷大。所以,退而求其次,我们用 $|z|<2$ 作为迭代的继续条件。
通过对在不同迭代深度终止的点填充不同的颜色,我们就可以得到类似上面展示的美丽图片。
下面的程序是我大一练习 C 语言的时候写的,我把它捡出来并简单加了一些注释。这个程序实现使用CPU计算上面两个集合的图像并输出到BMP文件。(关于输出到BMP文件,可以参考 用C++画图(一):图片文件)
#include<stdio.h>
//复数
struct complex
{
double Real;
double Imag;
};
//颜色
struct BGR
{
unsigned char B;
unsigned char G;
unsigned char R;
};
int Width, Height, max_Iterations, mode;
double X_max, X_min, Y_max, Y_min, Delta, xC, yC;
struct BGR IMG[2000 * 3000], Color[257];
//生成颜色序列
void Build_color_array()
{
int i;
for (i = 1;i <= 256;i++)
{
Color[(i) % 256 + 1].B = i % 256 / 64 == 0 ? 3 * i : i % 256 / 64 == 1 ? 128 + i : i % 256 / 64 == 2 ? -4 * i - 1 : 0;
Color[(i) % 256 + 1].G = i % 256 / 32 == 0 ? i : i % 256 / 32 == 1 || i % 256 / 32 == 2 ? -64 + 3 * i : i % 256 / 32 == 3 ? 128 + i : i % 256 / 32 == 4 ? 383 - i : i % 256 / 32 == 5 || i % 256 / 32 == 6 ? 703 - 3 * i : 255 - i;
Color[(i) % 256 + 1].R = i % 256 / 64 == 0 ? i : i % 256 / 64 == 1 ? -128 + 3 * i : i % 256 / 64 == 2 ? 383 - i : 768 - 3 * i;
}
Color[0].B = Color[0].G = Color[0].R = 0;
}
struct complex plus(struct complex A, struct complex B)
{
struct complex C;
C.Real = A.Real + B.Real;
C.Imag = A.Imag + B.Imag;
return C;
}
struct complex multi(struct complex A, struct complex B)
{
struct complex C;
C.Real = A.Real * B.Real - A.Imag * B.Imag;
C.Imag = A.Real * B.Imag + A.Imag * B.Real;
return C;
}
struct complex power(struct complex A, int n)
{
struct complex C = A;
int i;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
C = multi(C, A);
return C;
}
//迭代函数
struct complex f(struct complex Z, struct complex C)
{
return plus(power(Z, 2), C);
}
//绘制图片
void draw_img()
{
struct complex C, Z;
double Delta_X = (X_max - X_min) / Width;
double Delta_Y = (Y_max - Y_min) / Height;
double a, b;
if (!mode)
{
printf("Julia Pos: ");
scanf("%lf%lf", &a, &b);
}
int r, c, i, s = 0;
system("cls");
printf("Processing ");
for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++) putchar(' ');
printf("|%2d%%", s);
for (r = 1; r <= Height; r++)
{
for (c = 1; c <= Width; c++)
{
if (mode)
{
C.Real = X_min + c * Delta_X;
C.Imag = Y_min + r * Delta_Y;
Z.Real = Z.Imag = 0;
}
else
{
C.Real = a;
C.Imag = b;
Z.Real = X_min + c * Delta_X;
Z.Imag = Y_min + r * Delta_Y;
}
for (i = 1; i <= max_Iterations; i++)
{
Z = f(Z, C);
if (Z.Real * Z.Real + Z.Imag * Z.Imag > 4.0)
{
IMG[(r - 1) * Width + c - 1] = Color[i % 256 + 1];
break;
}
}
}
if (r == (int)((Height / 100.0) * (int)(r / (Height / 100.0))) + 1)
{
s++;
system("cls");
printf("Processing ");
for (i = 1;i <= s;i++) putchar('.');
for (i = s + 1;i <= 100;i++) putchar(' ');
printf("|%2d%%", s);
}
}
}
//输出到BMP
void Save_to_Bmp(const char* filename)
{
unsigned int size = Width * Height * 3 + 54;
unsigned short head[] = {
0x4D42,size % 0x10000,size / 0x10000,0,0,0x36,0,0x28,
0,Width % 0x10000,Width / 0x10000,Height % 0x10000,Height / 0x10000,0x10,0x18,0,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0
};
printf("\nExporting...\n");
FILE* fp = fopen(filename, "wb");
if (!fp)
{
printf("ERROR: cannot open file.\n");
return;
}
fwrite(head, 1, sizeof(head), fp);
fwrite(IMG, 1, size, fp);
fclose(fp);
}
main()
{
printf("Fractal\n");
printf("Select Mode (1 for Mandelbrot; 0 for Julia): ");
scanf("%d", &mode);
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d %d", &Width, &Height);
printf("Zone Width: ");
scanf("%lf", &Delta);
printf("Center: ");
scanf("%lf%lf", &xC, &yC);
printf("Max Iteration: ");
scanf("%d", &max_Iterations);
X_max = xC + Delta / 2;
X_min = xC - Delta / 2;
Y_max = yC + Delta / 2 * Height / Width;
Y_min = yC - Delta / 2 * Height / Width;
Build_color_array();
draw_img();
Save_to_Bmp("../data/Picture.bmp");
printf("Done.\n");
getchar();
while (getchar() != 10);
}
并行计算
如果你编译并运行了上面的代码,你会发现,运行所消耗的时间非常漫长,尽管生成的美丽图片使得它不那么难以忍受。
如何加快运行的速度呢?不难发现,在上面两种分形集合的生成中,像素间是两两独立的,他们不使用相同的计算资源也不存在逻辑上的前后关系。也就是说,将两个像素的计算任务交给不同的计算单元同时运算,结果和简单的让一个计算单元依次计算并不会有什么不同。显然,如果能同时使用多个计算单元来计算,速度将大大提高,这也就是并行计算的思想。
现代计算机的CPU通常拥有多于一个的核心(比如我的笔记本使用的 i5-8250U 就拥有四个核心),如果能将其全部用上,就能提高运行的速度。但是,计算机上还有一个模块拥有更多的计算单元——GPU。
GPU指图形处理单元,也就是显卡。在计算机图形的渲染中,对每个像素的着色也是独立进行的,具有高度的并行性。作为图形渲染的专用硬件,GPU理所应当的具有强大的并行处理能力。事实上,GPU便是由成百上千的小计算单元组成。
现代的GPU通常拥有可编程计算的能力,可以用来计算用户指定的任务,我们可以使用它的并行计算能力来加速我们的计算。
并行程序实现
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture),是显卡厂商 NVIDIA 推出的运算平台。我们使用它来对分形问题进行并行加速。
此外,为了使用 GUI 和鼠标交互,我使用 OpenGL 来生成窗口并渲染计算生成的图片。
有关资料:
CUDA与OpenGL交互开发_ruby97的专栏-CSDN博客
CUDA 部分:
#include "kernel.h"
#include "complex.h"
__global__ void MandelbrotKernel(uchar4* img, uchar3* palette, int2 size, double4 zone, int max_Iterations)
{
int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (index >= size.x * size.y) return;
int xIdx = index % size.x;
int yIdx = index / size.x;
double x = zone.x * (size.x - xIdx) / size.x + zone.z * xIdx / size.x;
double y = zone.y * (size.y - yIdx) / size.y + zone.w * yIdx / size.y;
double2 z = { 0, 0 };
double2 c = { x, y };
for (int i = 0; i < max_Iterations; i++)
{
z = complexPlus(complexSquare(z), c);
if (complexLength2(z) > 4.0)
{
img[index].x = palette[i % 256].x;
img[index].y = palette[i % 256].y;
img[index].z = palette[i % 256].z;
img[index].w = 255;
return;
}
}
img[index].x = 0;
img[index].y = 0;
img[index].z = 0;
img[index].w = 255;
}
__global__ void JuliaKernel(uchar4* img, uchar3* palette, int2 size, double2 con, double4 zone, int max_Iterations)
{
int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (index >= size.x * size.y) return;
int xIdx = index % size.x;
int yIdx = index / size.x;
double x = zone.x * (size.x - xIdx) / size.x + zone.z * xIdx / size.x;
double y = zone.y * (size.y - yIdx) / size.y + zone.w * yIdx / size.y;
double2 z = { x, y };
double2 c = { con.x, con.y };
for (int i = 0; i < max_Iterations; i++)
{
z = complexPlus(complexSquare(z), c);
if (complexLength2(z) > 4.0)
{
img[index].x = palette[i % 256].x;
img[index].y = palette[i % 256].y;
img[index].z = palette[i % 256].z;
img[index].w = 255;
return;
}
}
img[index].x = 0;
img[index].y = 0;
img[index].z = 0;
img[index].w = 255;
}
void Mandelbrot(uchar4* img, uchar3* palette, int2 size, double4 zone, int max_Iterations)
{
MandelbrotKernel << <ceil(size.x * size.y / 1024), 1024 >> > (img, palette, size, zone, max_Iterations);
}
void Julia(uchar4* img, uchar3* palette, int2 size, double2 con, double4 zone, int max_Iterations)
{
JuliaKernel << <ceil(size.x * size.y / 1024), 1024 >> > (img, palette, size, con, zone, max_Iterations);
}
C++ 部分:
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include <cuda_gl_interop.h>
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include "kernel.h"
int2 size = { 1920, 1080 }; //窗口(图像)尺寸
double diagonal = sqrt(size.x * size.x + size.y * size.y); //对角线
typedef struct
{
double zoom;
double xC;
double yC;
} Zone;
std::vector<Zone> zones; //可视区域栈
bool mode; //模式
int max_Iterations; //最大迭代数
double2 JuliaPos; //Julia集位置参数
uchar3 palette[256]; //调色板
uchar3* palette_d; //GPU端调色板数据指针
GLuint PBO; //OpenGL像素缓冲对象
cudaGraphicsResource* resource; //CUDA图形资源对象
bool mousePressed = false; //鼠标状态flag
double2 start, end; //鼠标控制点位置
void refreshImage(GLFWwindow* window);
//窗口大小改变回调
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
//更新数据
size.x = width;
size.y = height;
diagonal = sqrt(width * width + height * height);
//更新视口和像素缓冲对象
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glOrtho(0, size.x, size.y, 0, -1, 1);
glBufferData(GL_PIXEL_UNPACK_BUFFER, size.x * size.y * 4, NULL, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
refreshImage(window);
}
//鼠标点击回调
void mouse_button_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int button, int action, int mods)
{
if (button == GLFW_MOUSE_BUTTON_LEFT)
{
if (action == GLFW_PRESS && !mousePressed)
{
//左键按下:初始化控制点
mousePressed = true;
glfwGetCursorPos(window, &start.x, &start.y);
end = start;
}
else if (action == GLFW_RELEASE && mousePressed)
{
//左键抬起:计算新视口,刷新
Zone temp = zones.back();
mousePressed = false;
double xC = temp.xC + (start.x - size.x / 2.0) / size.x * temp.zoom;
double yC = temp.yC - (start.y - size.y / 2.0) / size.x * temp.zoom;
double zoom = temp.zoom * sqrt(pow(start.x - end.x, 2) + pow(start.y - end.y, 2)) * 2 / diagonal;
zones.push_back({ zoom, xC, yC });
refreshImage(window);
}
}
if (button == GLFW_MOUSE_BUTTON_RIGHT && action == GLFW_RELEASE)
{
if (!mousePressed && zones.size() > 1)
{
//右键:回退视口
zones.pop_back();
refreshImage(window);
}
else
{
//右键:取消控制
mousePressed = false;
refreshImage(window);
}
}
}
//鼠标移动回调
static void cursor_position_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos)
{
if (mousePressed)
{
//更新控制点
end.x = xpos;
end.y = ypos;
//计算示意框
double len = sqrt(pow(start.x - end.x, 2) + pow(start.y - end.y, 2));
double x = len * size.x / diagonal;
double y = len * size.y / diagonal;
//绘制示意框
glDrawPixels(size.x, size.y, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, 0);
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP);
glColor4f(1, 0, 0, 1);
glVertex2d(start.x + x, start.y + y);
glVertex2d(start.x + x, start.y - y);
glVertex2d(start.x - x, start.y - y);
glVertex2d(start.x - x, start.y + y);
glEnd();
glFlush();
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
}
}
//ESC退出
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
}
//初始化调色板
void initPalette()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
palette[i % 256].x = i % 256 / 64 == 0 ? i : i % 256 / 64 == 1 ? -128 + 3 * i : i % 256 / 64 == 2 ? 383 - i : 768 - 3 * i;
palette[i % 256].y = i % 256 / 32 == 0 ? i : i % 256 / 32 == 1 || i % 256 / 32 == 2 ? -64 + 3 * i : i % 256 / 32 == 3 ? 128 + i : i % 256 / 32 == 4 ? 383 - i : i % 256 / 32 == 5 || i % 256 / 32 == 6 ? 703 - 3 * i : 255 - i;
palette[i % 256].z = i % 256 / 64 == 0 ? 3 * i : i % 256 / 64 == 1 ? 128 + i : i % 256 / 64 == 2 ? -4 * i - 1 : 0;
}
cudaMalloc((void**)&palette_d, 256 * sizeof(uchar3));
cudaMemcpy(palette_d, palette, 256 * sizeof(uchar3), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
}
//刷新图像
void refreshImage(GLFWwindow* window)
{
//CUDA映射GPU端图形资源
uchar4* img_d;
cudaGraphicsGLRegisterBuffer(&resource, PBO, cudaGraphicsMapFlagsNone);
cudaGraphicsMapResources(1, &resource, NULL);
cudaGraphicsResourceGetMappedPointer((void**)&img_d, NULL, resource);
//计算可视区域
Zone z = zones.back();
double4 zone;
zone.x = z.xC - z.zoom / 2;
zone.z = z.xC + z.zoom / 2;
zone.y = z.yC - z.zoom / 2 * size.y / size.x;
zone.w = z.yC + z.zoom / 2 * size.y / size.x;
//CUDA计算
if (mode)
Mandelbrot(img_d, palette_d, size, zone, max_Iterations);
else
Julia(img_d, palette_d, size, JuliaPos, zone, max_Iterations);
// Check for any errors launching the kernel
cudaError_t cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess)
{
std::cerr << "addKernel launch failed: " << cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus) << std::endl;
exit(-1);
}
//CUDA图形资源解映射
cudaGraphicsUnmapResources(1, &resource, NULL);
//OpenGL绘制像素
glDrawPixels(size.x, size.y, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, 0);
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
}
int main()
{
//初始区域
zones.push_back({ 4, 0, 0 });
std::cout << "Fractal with OpenGL and CUDA\n";
std::cout << "Select Mode (1 for Mandelbrot; 0 for Julia): ";
std::cin >> mode;
std::cout << "Max Iteration: ";
std::cin >> max_Iterations;
if (!mode)
{
std::cout << "Julia Pos: ";
std::cin >> JuliaPos.x >> JuliaPos.y;
}
//初始化OpenGL到兼容模式
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_COMPAT_PROFILE);
//创建窗口
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(size.x, size.y, "Fractal", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
//初始化OpenGL API
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
//初始化视口
glViewport(0, 0, size.x, size.y);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glOrtho(0, size.x, size.y, 0, -1, 1);
//绑定事件处理回调
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetMouseButtonCallback(window, mouse_button_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, cursor_position_callback);
//创建像素缓冲区
glGenBuffers(1, &PBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_PIXEL_UNPACK_BUFFER, PBO);
glBufferData(GL_PIXEL_UNPACK_BUFFER, size.x * size.y * 4, NULL, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
//初始化调色盘
initPalette();
//刷新图像
refreshImage(window);
//循环处理事件
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
processInput(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
更多
本文的代码保存在:JeffreyXiang/Fractal - GitHub
如果你对这个话题仍感兴趣,不妨看看下面几个链接。
