前言
前面的章节中,我们一步步走来,了解了图像的读取和输出,基本图形的绘制,图像的变换(平移、旋转、缩放)和文字的插入。在此基础上,今天我们终于可以写出第一个实用的画图程序——函数图像绘制。
原理
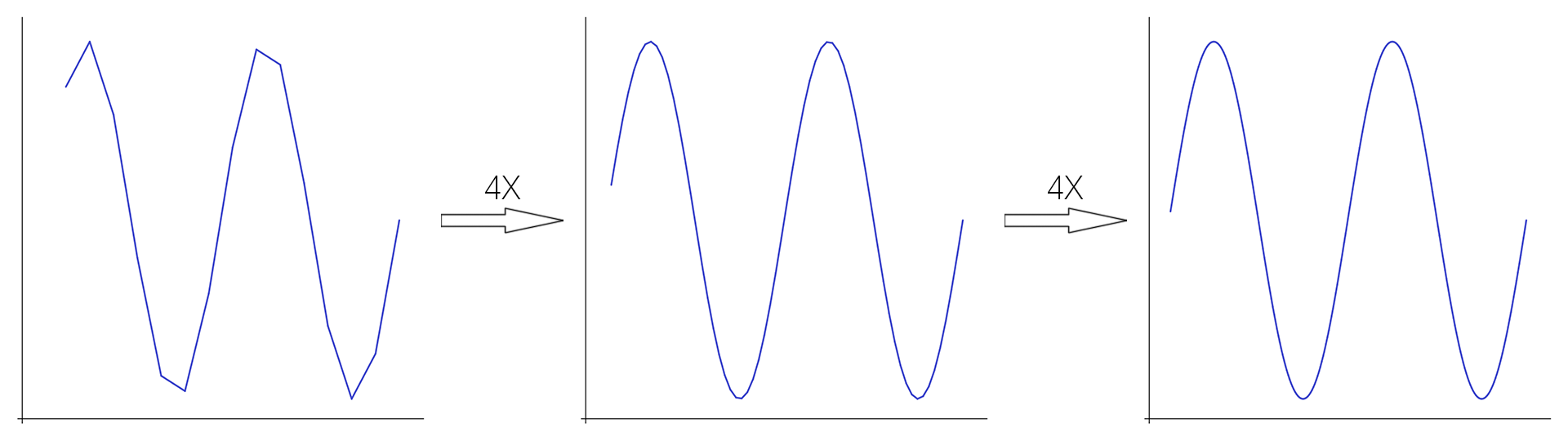
绘制函数图像,最简单的方法便是在原函数上取很多离散的点,再两两连线,绘制成折线图。当点取得足够密集时,图像看起来就是连续的。我们的函数图像绘制工具就是利用的这种方法,在相邻两点之间用胶囊体(Capsule)相连。
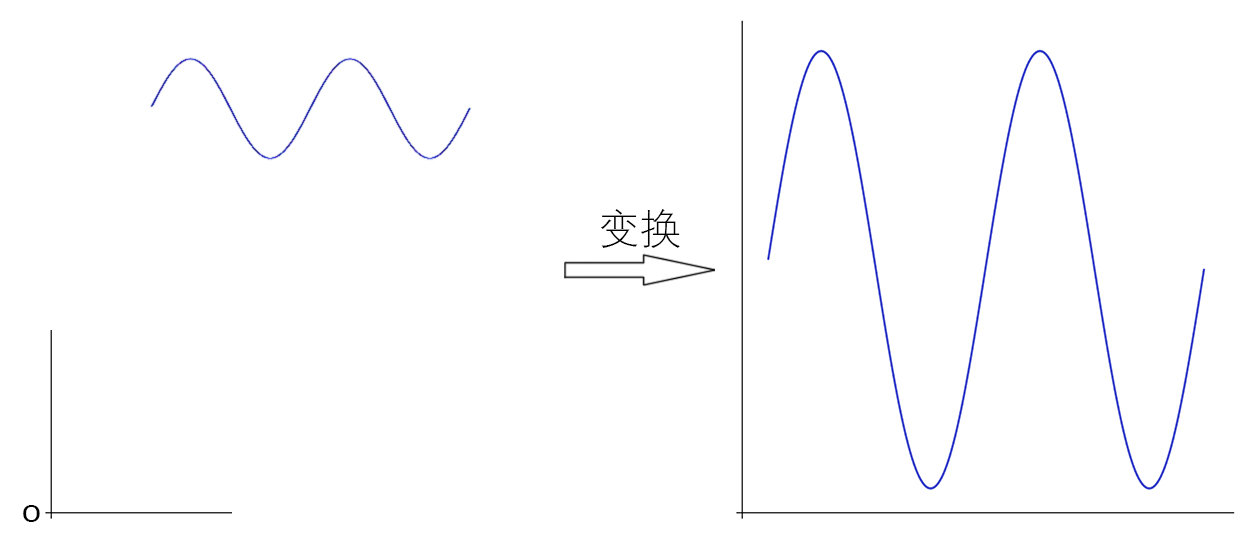
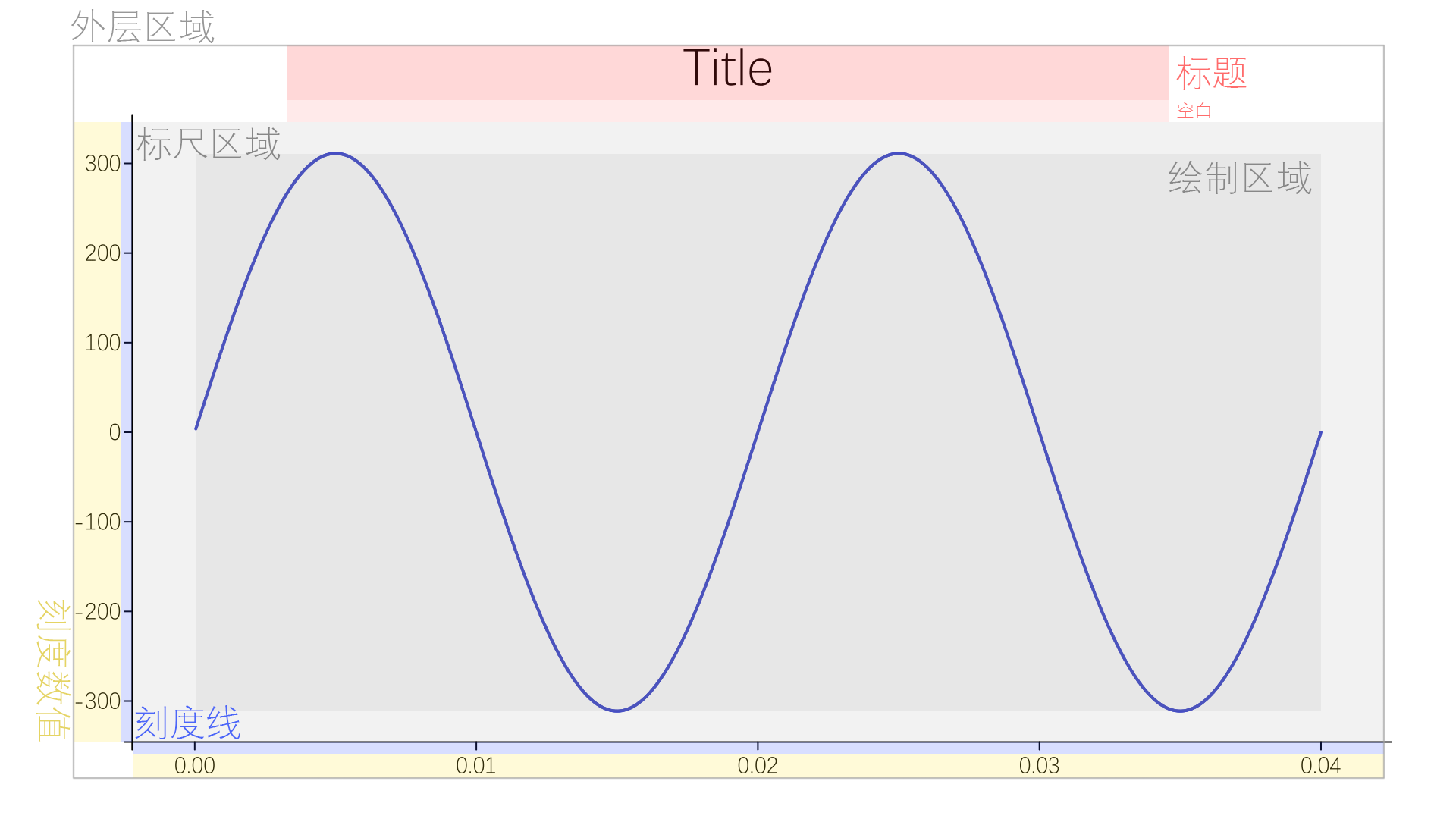
除了函数图像本身,最后生成的图片上还有一些其他的部分,比如标尺,刻度,标题,横纵轴的名字与单位等,这要求我们创建一个布局来给每个部分提供绘制的空间,最好可以由用户指定需要绘制哪些部件,布局也能够自适应地进行调整,不会出现空出未绘制部件的位置的情况。此外,还要考虑将图像有意义的部分保留,剔除空白的部分,即我们要根据函数的值域和定义域来确定函数的xy坐标与图片的像素坐标之间的对应关系,来使得最终函数图像区域能够集中绘制有意义的图像。
布局
根据一般的函数图像绘制标准(例如Origin软件中的格式),绘图区域是一个矩形,标尺围绕着绘图区域的左边和下边,和绘图区域之间有一定的空白。标尺上朝外画着刻度,并标有数值,从此再往外是两个坐标轴的名称,它们与刻度数值之间有一定空白。从标尺区域往上是标题,中间也有空白。
由此,我们可以抽象出下面的布局图:
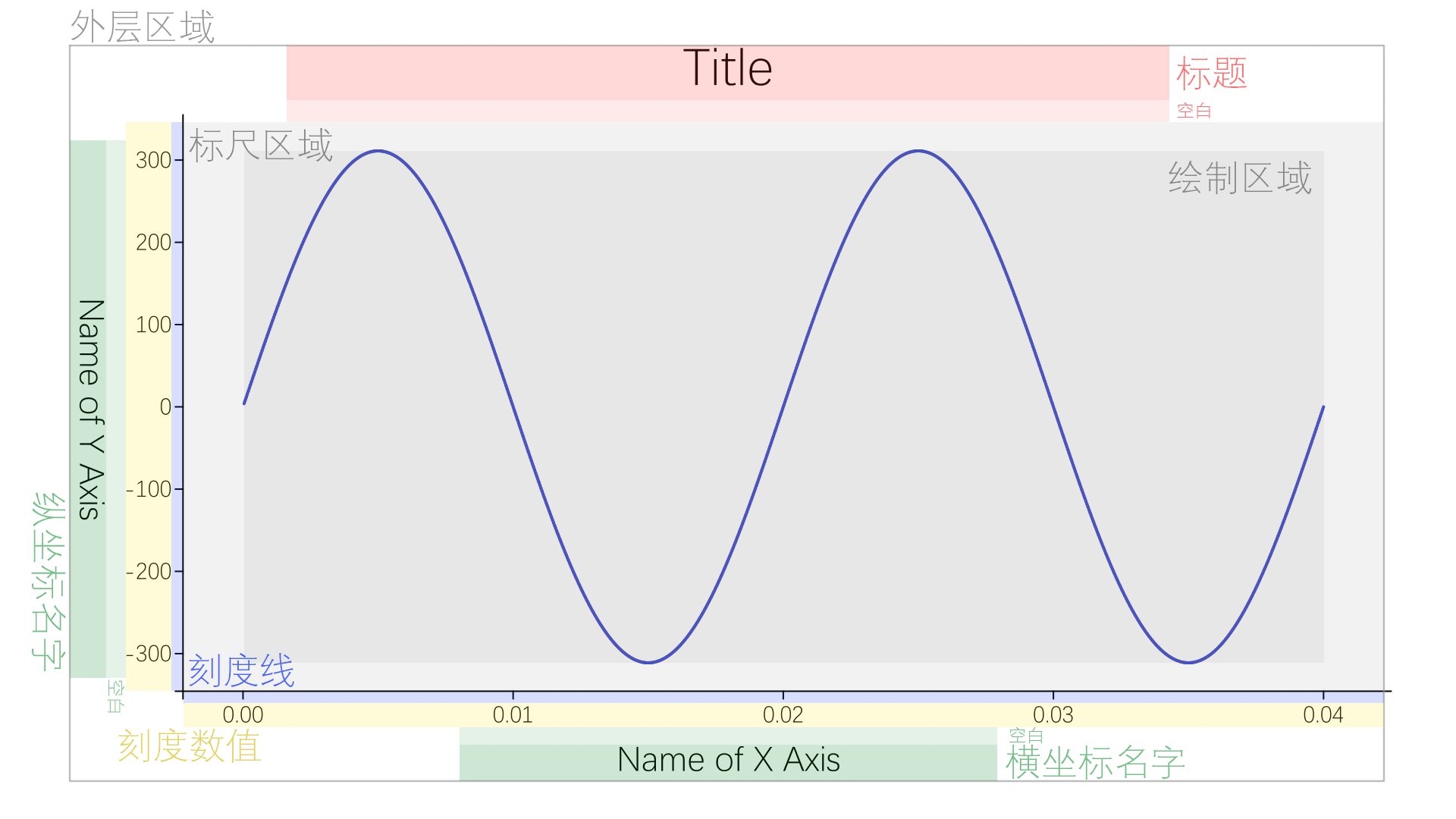
由于我们已经知道的是图片画布的大小,所以为了确定布局中每一块的位置,我们只能由外向内推导。
先确定外层区域的大小,这可以由画布的大小自定义推导得到,再计算出标题,横纵坐标名称,横纵坐标数值,横纵坐标刻度的宽度。需要注意的是,这些区域应该都是可选的,如果用户在外围不设置使用这些元素,我们应把它们的宽度设为0,这样就可以实现布局的自适应调整
例如我们不使用横纵轴的名称,对应的布局如下:
映射
为了实现上文中提到的另一个问题——只绘制函数有意义的部分,我们要根据函数的值域和定义域来确定函数的xy坐标与图片的像素坐标之间的对应关系,来使得最终函数图像区域能够集中绘制有意义的图像。这本质上就是求两个一维的线性映射,一个将定义域映射到绘制区域的宽度上,另一个将值域映射到绘制区域的高度上。这是很容易的。
我们令这个映射为 $f:x\rightarrow x$,其中:
\[x'=sx+d\]为了求这个映射,我们需要两个确定的对应关系。在这里就是定义域(值域)的上下限与绘制区域的边界坐标的对应关系:
\[\begin{gather} f(x_{min})=x'_{min}\quad f(x_{max})=x'_{max}\\ \Rightarrow\left\{\begin{split} &sx_{min}+d=x'_{min}\\ &sx_{max}+d=x'_{max} \end{split}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left\{\begin{split} &s=\frac{x'_{max}-x'_{min}}{x_{max}-x_{min}}\\ &d=\frac{x_{max}x'_{min}-x_{min}x'_{max}}{x_{max}-x_{min}} \end{split}\right. \end{gather}\]按此公式的指引,我们就能够将函数有意义的部分映射到绘制区域里了。
刻度与文字
刻度的生成就非常的容易且随意,你可以根据定义域(值域)的宽度,用你认为合适的方法获得刻度的间隔,再利用整除等方式获得一列需要标注的数值,最后利用上面的映射来获取它在轴上的坐标,绘制即可。
标注刻度的数值需要将浮点型转化为字符串,这可以使用std::stringstream来轻松完成,还能够像std::cout一样设置保留小数与科学计数法。
注意,布局中的纵轴刻度数值区域的宽度,也应该用每个刻度的数值对应的文字在图中的长度的最大值来计算。使用固定数值不会产生很好的效果.
其他的标题、横纵轴的名称的绘制,主要是要求对齐和居中,利用上一节中锚点在插入图中的比例位置这个参数,可以轻松搞定。
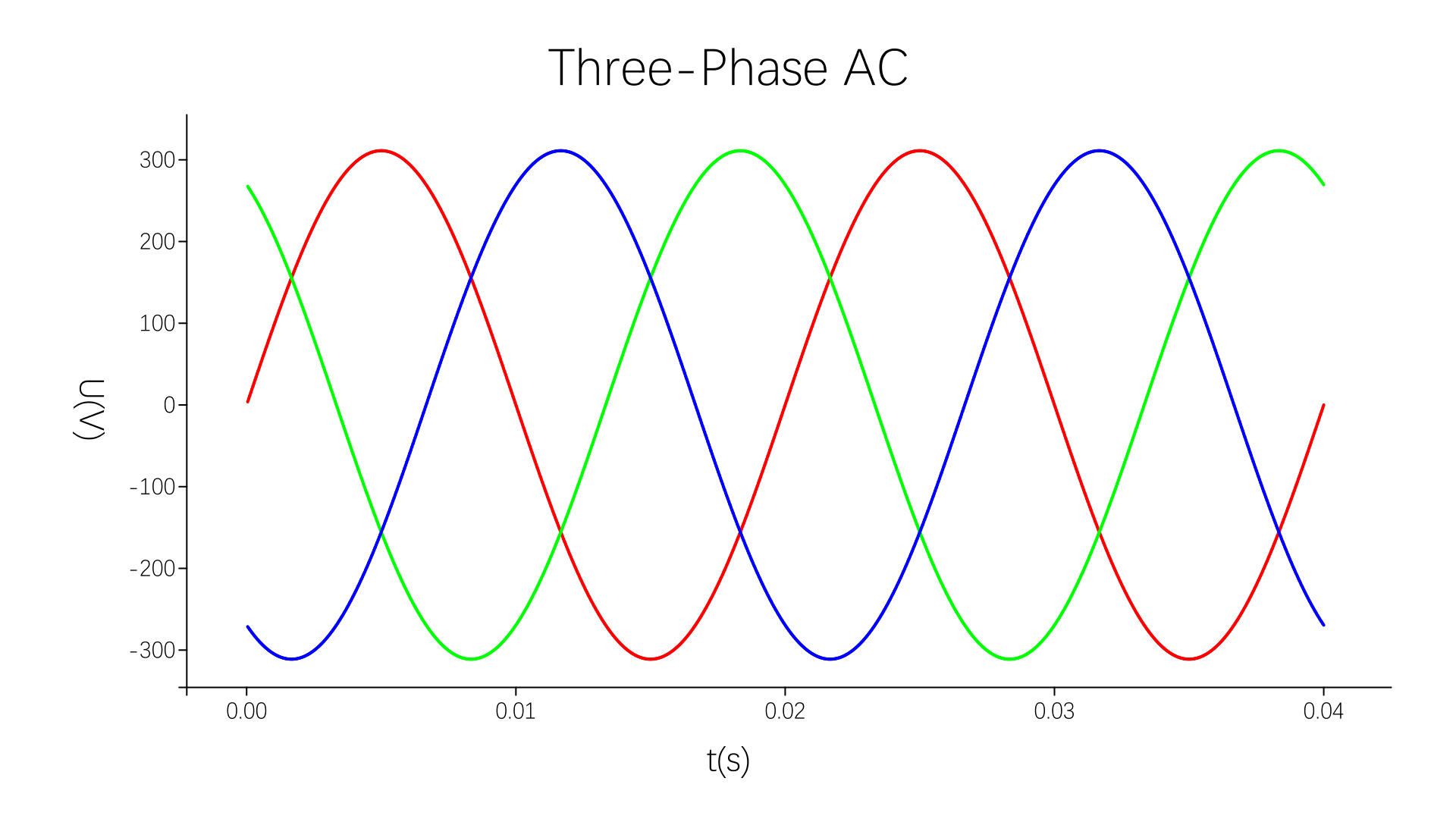
最终成果:
代码
class Plot
{
public:
enum ERROR { FONT_NOT_SET };
//图表上的文字标签
typedef struct
{
char* text;
Color color;
Font* font;
double height;
} Lable;
//连续数据
typedef struct
{
function<double(double)> func;
Color color;
double lineWidth;
} Continuous;
//离散数据
typedef struct
{
double* data;
Color color;
double lineWidth;
} Discrete;
private:
static const int defTitleH = 72;
static const int defNameH = 48;
static const int defNumberH = 32;
static const int defWidth = 1920;
static const int defHeight = 1080;
int width;
int height;
Lable title; //图表标题
Lable verName; //纵轴名字
Lable horName; //横轴名字
Color rulerColor; //标尺颜色
Font* rulerFont; //标尺字体
double rulerHeight; //标尺字体高度
bool verScaleEnabled; //显示刻度
bool horScaleEnabled;
bool verNumberEnabled; //显示数字
bool horNumberEnabled;
Font* defFont; //默认字体
//核心函数,负责利用离散数据点绘制图像
void plotRaw(Image& image, vector<Discrete> data, int points, double xMin, double xMax)
{
if (defFont == NULL)
{
cerr << "ERROR | Plot::plotRaw(Image&, vector<Discrete>, int, double, double) : Default font not set.\n";
throw FONT_NOT_SET;
}
//初始化字体
if (!title.font) title.font = defFont;
if (!verName.font) verName.font = defFont;
if (!horName.font) horName.font = defFont;
if (!rulerFont) rulerFont = defFont;
//获取极值、极值差(最小2e-6)
double yMax = data[0].data[0], yMin = yMax;
for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < points; j++)
{
yMax = max(yMax, data[i].data[j]);
yMin = min(yMin, data[i].data[j]);
}
}
if (yMax - yMin < 2e-6)
{
yMax += 1e-6;
yMin -= 1e-6;
}
int om ; //数量级
double step; //刻度间隔
double pos; //刻度像素位置
stringstream str; //刻度数值缓冲区
//计算纵轴刻度数值区域宽度
double verNumW = 0;
if (verScaleEnabled && verNumberEnabled)
{
om = round(log10(yMax - yMin) - 1); //数量级
step = pow(10, om); //标注间隔
//计算最大的刻度数值宽度作为区域宽度
for (int y = round(yMin / step); y <= round(yMax / step); y++)
{
str << fixed << setprecision(-om > 0 ? -om : 0) << y * step;
verNumW = max(rulerFont->stringWidth(str.str(), rulerHeight), verNumW);
str.str("");
}
}
//计算横轴刻度数值区域宽度
double horNumW = (horScaleEnabled && horNumberEnabled) ? rulerHeight : 0;
//计算刻度线宽度
double verSclW = verScaleEnabled ? 15 : 0;
double horSclW = horScaleEnabled ? 15 : 0;
//计算文字标签宽度
double titleW = title.text ? 1.5 * title.height : 0;
double verNameW = verName.text ? 1.5 * verName.height : 0;
double horNameW = horName.text ? 1.5 * horName.height : 0;
//设置外层区域参数
double outXMin = max(25.0, 0.05 * image.getWidth());
double outXMax = image.getWidth() - outXMin;
double outYMin = max(25.0, 0.05 * image.getHeight());
double outYMax = image.getHeight() - outYMin;
//设置标尺区域参数
double rulerXMin = outXMin + verNameW + verNumW + verSclW;
double rulerXMax = outXMax;
double rulerYMin = outYMin + horNameW + horNumW + horSclW;
double rulerYMax = outYMax - titleW;
//设置绘制区域参数
double plotXMin = rulerXMin + 0.05 * (rulerXMax - rulerXMin);
double plotXMax = rulerXMax - 0.05 * (rulerXMax - rulerXMin);
double plotYMin = rulerYMin + 0.05 * (rulerYMax - rulerYMin);
double plotYMax = rulerYMax - 0.05 * (rulerYMax - rulerYMin);
//创建函数值到像素位置的映射(x' = s * x + d)
double ys, yd, xs, xd;
ys = (plotYMax - plotYMin) / (yMax - yMin);
yd = -ys * yMin + plotYMin;
xs = (plotXMax - plotXMin) / (xMax - xMin);
xd = -xs * xMin + plotXMin;
//准备工作
Capsule* cap; //直线对象
Figure::Attribute rulerAttr = { rulerColor, 0, -1 };
image.setBackgroundColor({ 0, 0, 0, 0 });
//画坐标轴
cap = new Capsule({ rulerXMin - 10, rulerYMin }, { rulerXMax + 10, rulerYMin }, 1, rulerAttr);
image.draw(*cap);
delete cap;
cap = new Capsule({ rulerXMin, rulerYMin - 10 }, { rulerXMin, rulerYMax + 10 }, 1, rulerAttr);
image.draw(*cap);
delete cap;
//数值标注
if (verScaleEnabled)
{
om = round(log10(yMax - yMin) - 1); //数量级
step = pow(10, om); //标注间隔
for (int y = floor(yMin / step); y <= ceil(yMax / step); y++)
{
pos = ys * y * step + yd; //计算刻度的图上坐标
if (pos > rulerYMin && pos < rulerYMax)
{
//绘制刻度线
cap = new Capsule({ rulerXMin, pos }, { rulerXMin - 10, pos }, 1, rulerAttr);
image.draw(*cap);
delete cap;
if (verNumberEnabled)
{
//绘制刻度数值
str << fixed << setprecision(-om > 0 ? -om : 0) << y * step;
image.addText(str.str(), { rulerXMin - 15, pos }, { 1, 0.5 }, rulerHeight, 0, *rulerFont, rulerColor);
str.str("");
}
}
}
}
if (horScaleEnabled)
{
om = round(log10(xMax - xMin) - 1);
step = pow(10, om);
for (int x = floor(xMin / step); x <= ceil(xMax / step); x++)
{
pos = xs * x * step + xd;
if (pos > rulerXMin && pos < rulerXMax)
{
cap = new Capsule({ pos, rulerYMin }, { pos, rulerYMin - 10 }, 1, rulerAttr);
image.draw(*cap);
delete cap;
if (horNumberEnabled)
{
str << fixed << setprecision(-om > 0 ? -om : 0) << x * step;
image.addText(str.str(), { pos, rulerYMin - 15 }, { 0.5, 1 }, rulerHeight, 0, *rulerFont, rulerColor);
str.str("");
}
}
}
}
//画标签
if (title.text)
image.addText(title.text, { width / 2.0, outYMax }, { 0.5, 1 }/*水平居中,顶部对齐*/, title.height, 0, *title.font, title.color);
if (verName.text)
image.addText(verName.text, { outXMin, height / 2.0 }, { 0.5, 0 }/*水平居中,底部对齐*/, verName.height, -90, *verName.font, verName.color);
if (horName.text)
image.addText(horName.text, { width / 2.0, outYMin }, { 0.5, 0 }/*水平居中,底部对齐*/, horName.height, 0, *horName.font, horName.color);
//画折线图
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
{
Figure::Attribute funcAttr = { data[i].color, 0, -1 };
double lwidth = data[i].lineWidth / 2;
for (int j = 1; j < points - 1; j++)
{
//计算函数上的坐标对应在图中的坐标
x1 = plotXMin + j * (plotXMax - plotXMin) / (points - 1);
y1 = ys * data[i].data[j] + yd;
x2 = plotXMin + (j + 1) * (plotXMax - plotXMin) / (points - 1);
y2 = ys * data[i].data[j + 1] + yd;
//连接一条直线
cap = new Capsule({ x1, y1 }, { x2, y2 }, lwidth, funcAttr);
image.draw(*cap);
delete cap;
}
}
}
public:
Plot() :
width(defWidth), height(defHeight), defFont(NULL),
title({ NULL, { 0, 0, 0 }, NULL, defTitleH }),
verName({ NULL, { 0, 0, 0 }, NULL, defNameH }),
horName({ NULL, { 0, 0, 0 }, NULL, defNameH }),
rulerColor(0, 0, 0), rulerHeight(defNumberH), rulerFont(NULL),
verScaleEnabled(true), horScaleEnabled(true),
verNumberEnabled(true), horNumberEnabled(true) {}
~Plot() {}
//设置输出尺寸
void setSize(int w, int h) { width = w; height = h; }
//设置默认字体
void setDefaultFont(Font& font) { defFont = &font; }
//设置标题
void setTitle(const char* text, Color color = { 0, 0, 0 }, double height = defTitleH, Font* font = NULL)
{ title.text = (char*)text; title.color = color; title.height = height; title.font = font; }
//设置纵轴名字
void setVerName(const char* text, Color color = { 0, 0, 0 }, double height = defNameH, Font* font = NULL)
{ verName.text = (char*)text; verName.color = color; verName.height = height; verName.font = font; }
//设置横轴名字
void setHorName(const char* text, Color color = { 0, 0, 0 }, double height = defNameH, Font* font = NULL)
{ horName.text = (char*)text; horName.color = color; horName.height = height; horName.font = font; }
//设置标尺
void setRuler(Color color = { 0, 0, 0 }, double height = defNumberH, Font* font = NULL)
{ rulerColor = color; rulerHeight = height; rulerFont = font; }
//设置纵轴刻度显示
void setVerScaleEnabled(bool enabled) { verScaleEnabled = enabled; }
//设置横轴刻度显示
void setHorScaleEnabled(bool enabled) { horScaleEnabled = enabled; }
//设置纵轴数字显示
void setVerNumberEnabled(bool enabled) { verNumberEnabled = enabled; }
//设置横轴数字显示
void setHorNumberEnabled(bool enabled) { horNumberEnabled = enabled; }
//画函数
Image plot(double xMin, double xMax, int points, vector<Continuous> funcs)
{
//生成散点数据
vector<Discrete> disc(funcs.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < funcs.size(); i++)
{
double* data = new double[points];
for (int j = 0; j < points; j++)
{
data[j] = funcs[i].func(xMin + (double)(xMax - xMin) * j / (points - 1));
}
disc[i] = { data, funcs[i].color, funcs[i].lineWidth };
}
//绘制折线图
Image image(width, height);
plotRaw(image, disc, points, xMin, xMax);
for (size_t i = 0; i < disc.size(); i++)
{
delete[] disc[i].data;
}
return image;
}
//画离散数据
Image plot(int points, vector<Discrete> data)
{
Image image(width, height);
plotRaw(image, data, points, 0, points);
return image;
}
};
也可以查看:🔗Github: JeffreyXiang/DrawWithCpp
总结
在本节中,我们分部解析了怎样利用现有的基础功能——图像的读取和输出,基本图形的绘制,图像的变换(平移、旋转、缩放)和文字的插入等——来实现我们的第一个应用小程序之函数图像绘制,成果颇丰,非常令人满意。
绘图工具 get!! Origin可以圆润的离开啦!
预告
也许真的要讲搁置已久的构造实体几何(CSG)了?无奖竞猜:我上次预告这一节是在哪篇文章?(/▽\)